The world doesn’t come with a manual. When you step outside the digital world there’s no set model of how things work or where to find them. Mostly our brains describe tangible things by relating them to something else.So why should data have a set model of rows and columns that doesn’t reflect the world it’s describing?
That’s why the most successful businesses of the last decade have moved away from those models and now use graphs to store and interact with their data. From social networking platforms, to search engines, media applications and even software building platforms.
Want to start your app project with us?
Book a demoSpeak with one of our product experts today.
By proceeding you agree to Builder.ai’s privacy policy and terms and conditions

What’s a graph database?
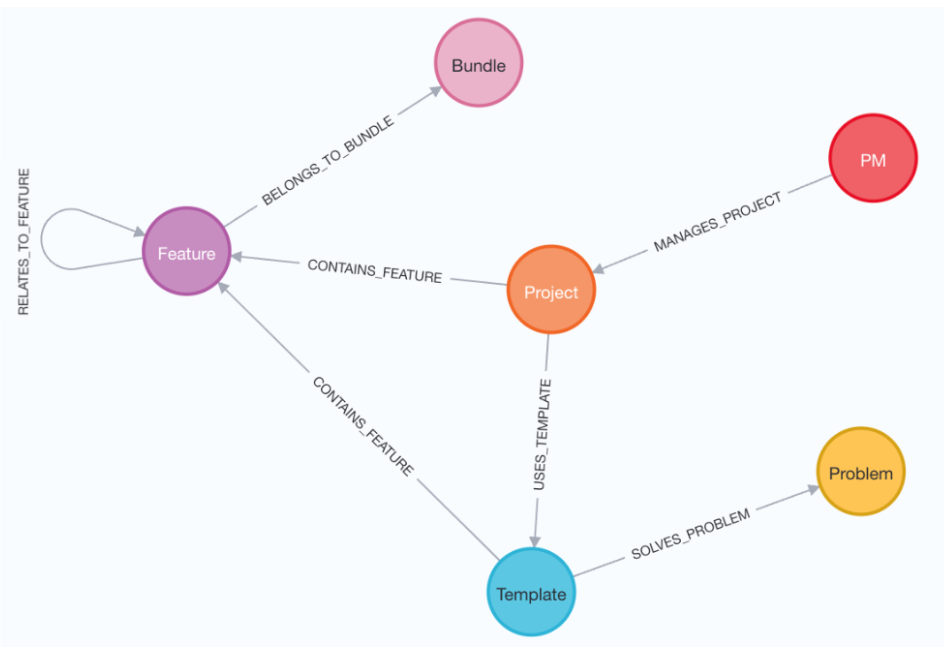
Graphs are a way of thinking about and storing data, they’re far better at showing interconnectivity than a traditional database. We think of the Builder Knowledge Graph as the brain of our operations, because it powers most of our workflows.
Nodes (the coloured circles below) represent the entities that exist within the Builder.ai ecosystem – from Features, to Templates, Problems and Projects. The edges (that’s the lines that connect nodes) on a graph represent how these nodes are related. For example, a feature can be included in your project as part of a template, while a template is responsible for solving a specific problem.
Next, you need graph embeddings
To harness the power of graphs, you need to help machines to be able to read and learn from your data.
We use graph embedding algorithms to do this. They transform the structural and attribute information from a graph, into numerical n-dimensional vectors. This means that now, machine learning algorithms can read the graph.
Then the fun begins. A graph-enabled machine learning algorithm automatically learns these numerical representations – and embeds information about each one and its most relevant connections.

So what can graphs do?
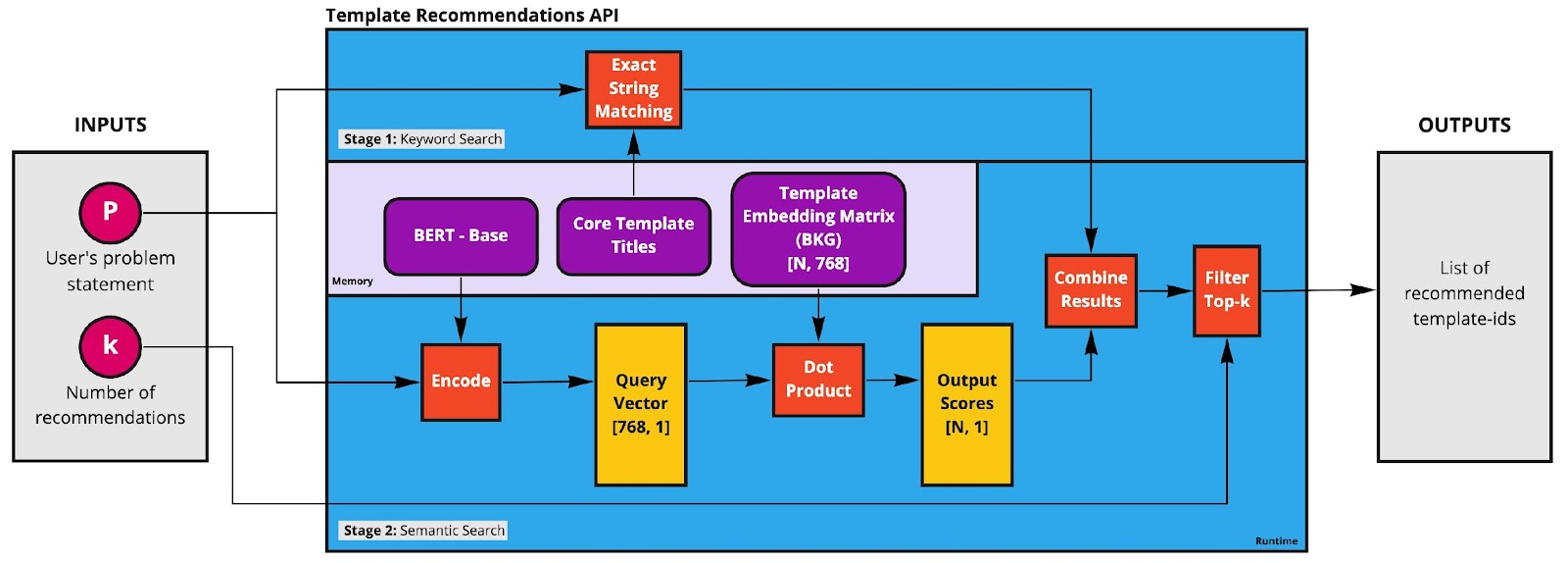
You give us a problem statement – by telling us what problem you want your app to solve. We combine natural language processing and graph-generated embeddings to recommend some project templates that could power your solution.
Can graphs recommend the best features too?
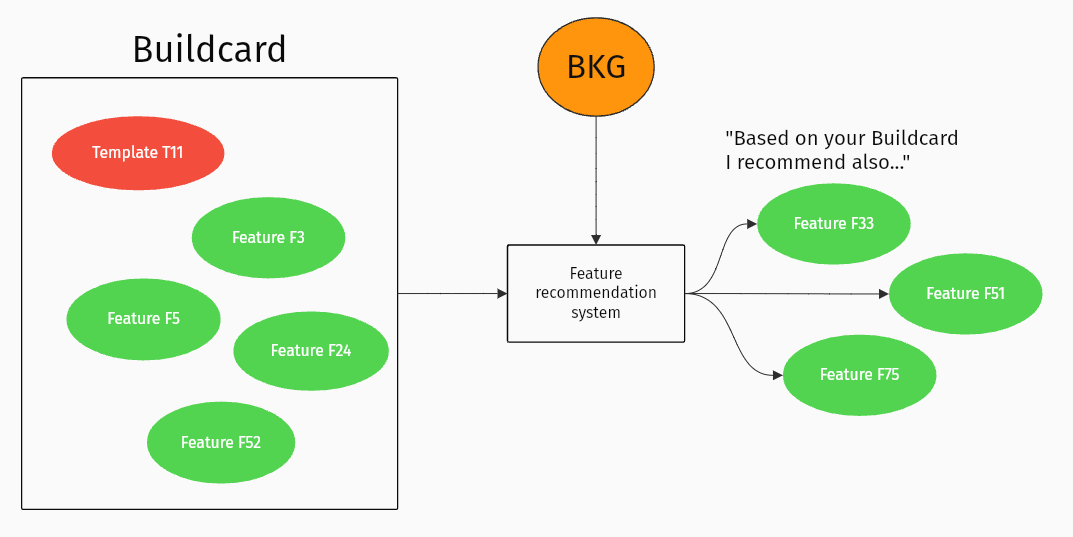
You can create a blueprint of your app idea by adding features (that’s things like Login, Push Notifications or Barcode Scanner) to your Buildcard™. It’s like adding toppings on a pizza. The Builder Knowledge Graph uses the template embeddings and feature embeddings that it’s learnt, to give you relevant recommendations – of extra features that could improve your app.
Image: A feature is recommended using the Builder Knowledge Graph (BKG)
Going beyond the graph
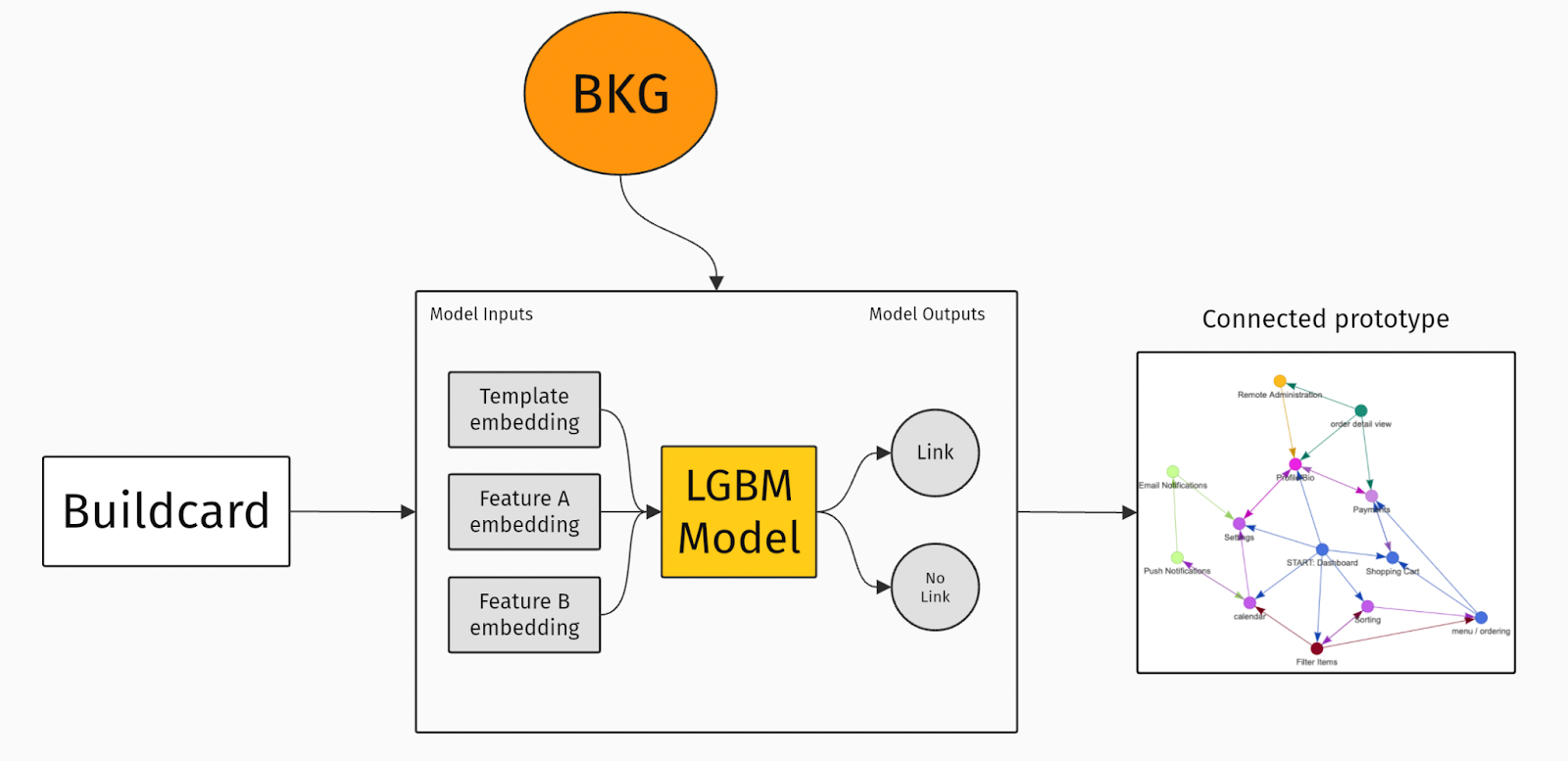
But can this technology create something new? Builder Now is our app prototyping tool (it helps you design your user journeys and improve your app, by offering instant app prototypes). Again, it’s only possible thanks to the numerical representations of features and templates that our graph has learned.
The Builder Knowledge Graph uses what it’s learned to spot relevant feature-to-feature connections – allowing it to automatically create a prototype for a completely new app.
Allocate work more efficiently
Historical data from all the projects we’ve ever done is fed into The Builder Knowledge Graph, which captures the complex interactions between features. These insights mean we can split a project up into parallel workstreams and have multiple people working on them at the same time – without holding each other up.
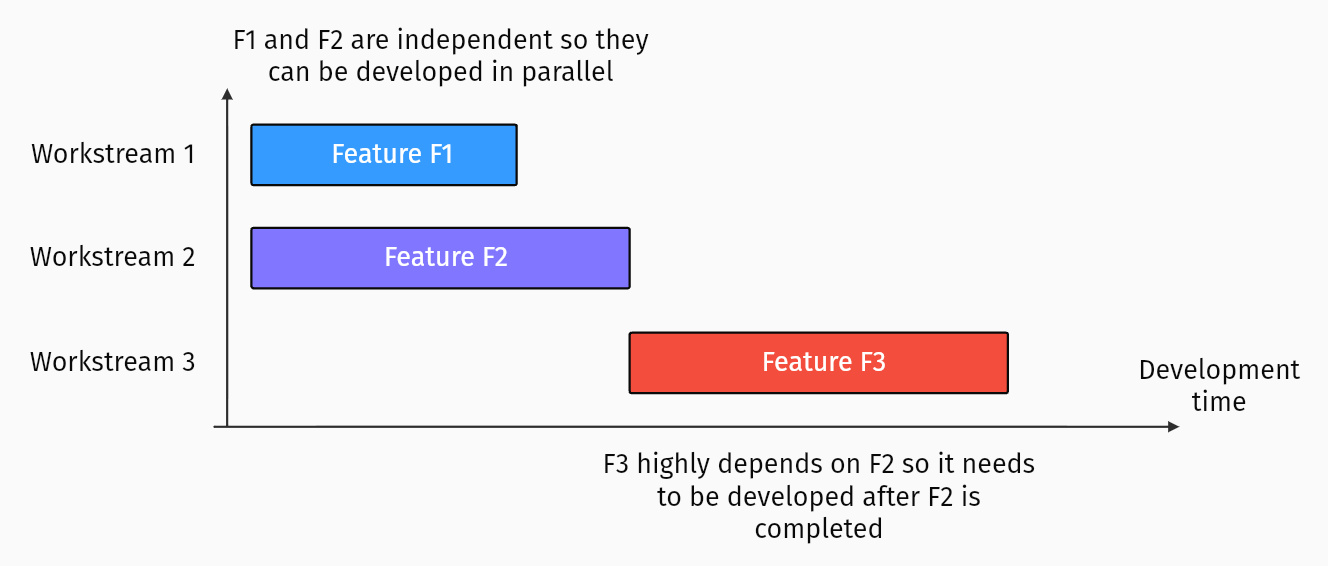
The right person for each job, instantly
And you can use these graph embeddings for any connections that are relevant to your business. Who works on every task of all our projects is also powered by our Builder Knowledge Graph.
For every designer or developer we work with – our embeddings work out their expertise level, past experience on similar features, and which timezone they’re in. Allocating work becomes automated based on each person’s merits, removing any bias.
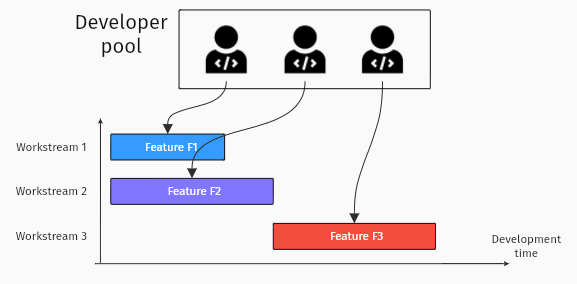
Selecting experts for different tasks, based on skills and experience
Spotting problems before they happen
Information from past projects stored in the Builder Knowledge Graph can work out the probability of your project being delayed too. It can also predict the most likely causes for a delay, for example, a customer is slow giving feedback, developers are raising more bugs, or feature to feature interactions are more complex. Then the Builder Knowledge Graph uses this insight to suggest actions that our project managers should take to avoid this delay.
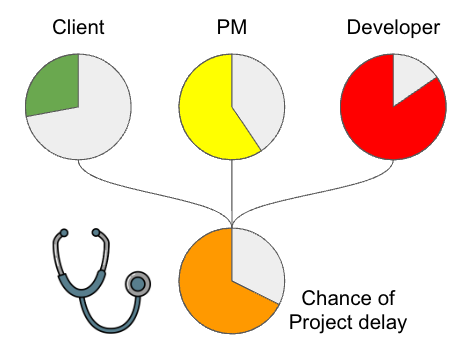
How will you use this power?
You’ve read how our own Builder Knowledge Graph is really the brain behind Builder.ai operations – allowing us to do everything from suggest relevant features to you, generate instant prototypes, work out who should do each task (and in what order). Hopefully this has given you a flavour of the power of graph databases. You’ve seen how using graph embeddings makes your data readable by machine learning algorithms. After that, your possibilities are wide open.
Dr. Andreas Antoniades is the graph machine learning lead at Builder.ai where he improves technology using his knowledge of data science, graphs and neural networks. Andreas has a PhD in Deep Learning and Neural Systems from the University of Surrey.







 Facebook
Facebook X
X LinkedIn
LinkedIn YouTube
YouTube Instagram
Instagram RSS
RSS


